Fantastic Info About How To Check Multicast Traffic
Another program required for testing needs to be started on the computer that will generate and send the network multicast traffic (multicastsend.exe).
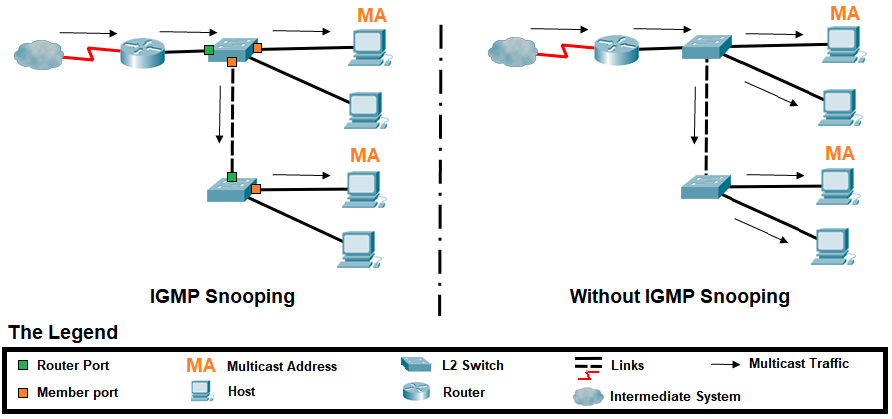
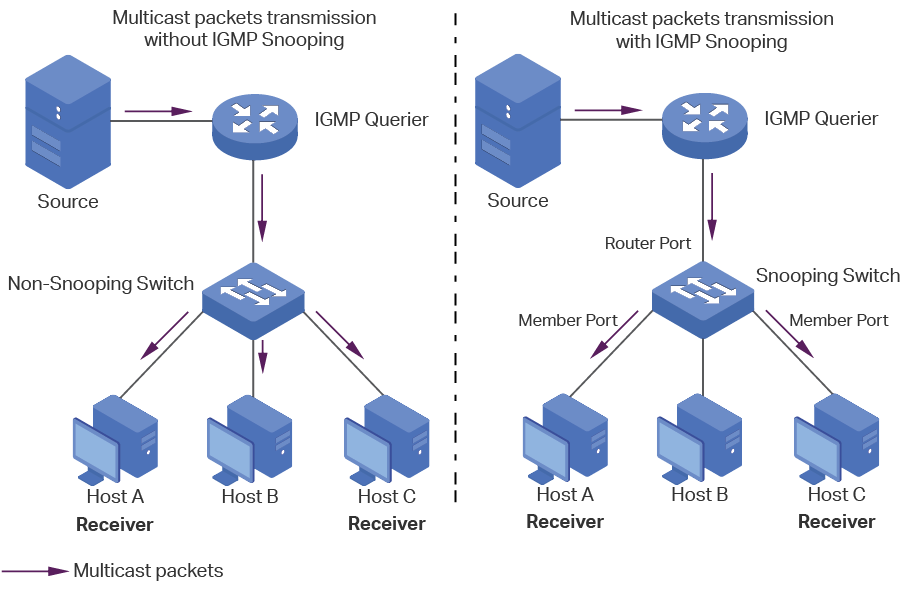
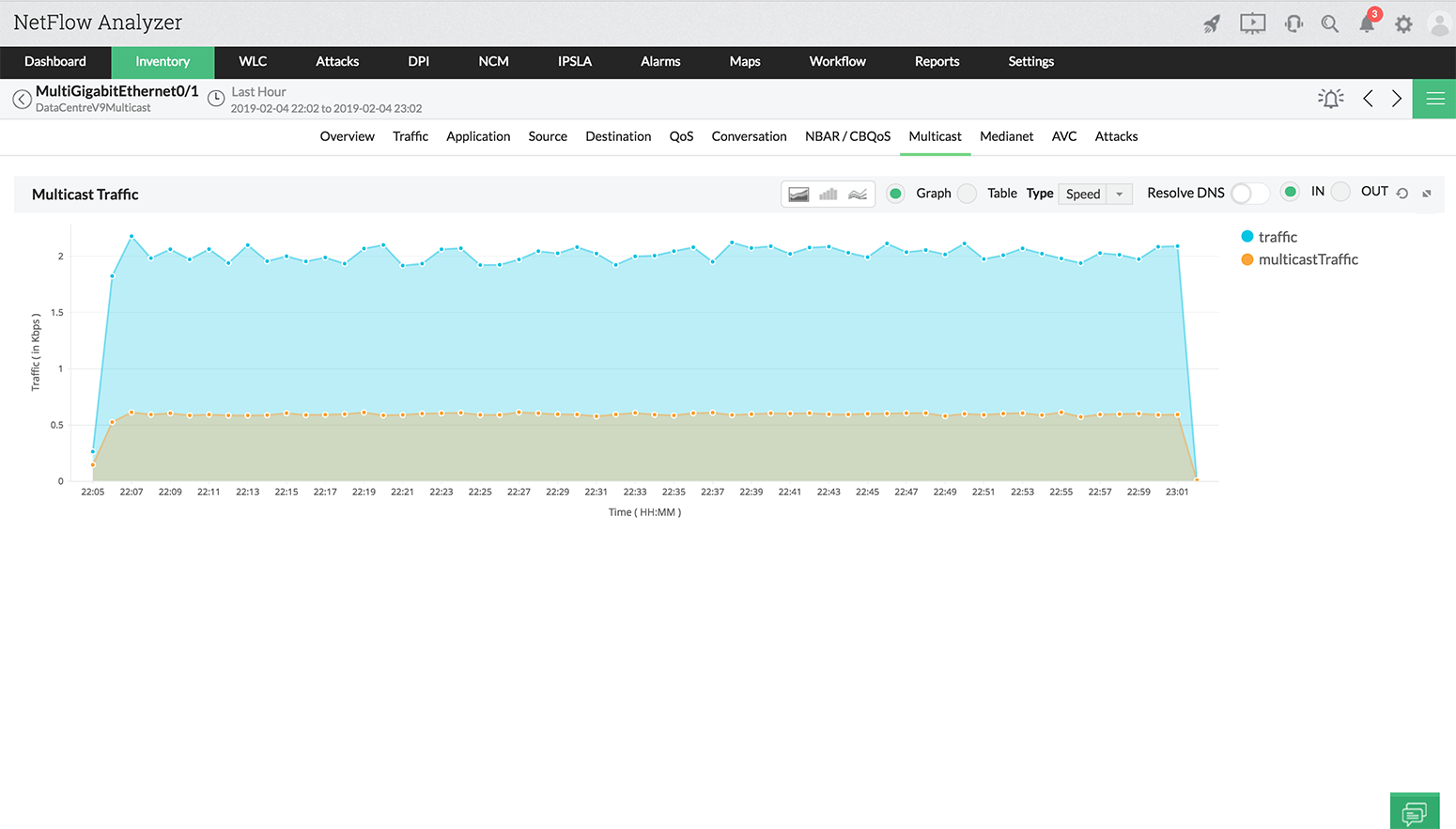
How to check multicast traffic. To display information about layer 2 igmp snooping multicast forwarding information base (fib) distribution, use the show forwarding distribution ip igmp snooping command. They must know the way to join and leave multicast groups and to propagate this information to multicast routers. Observe the traffic captured in the top wireshark packet list pane.
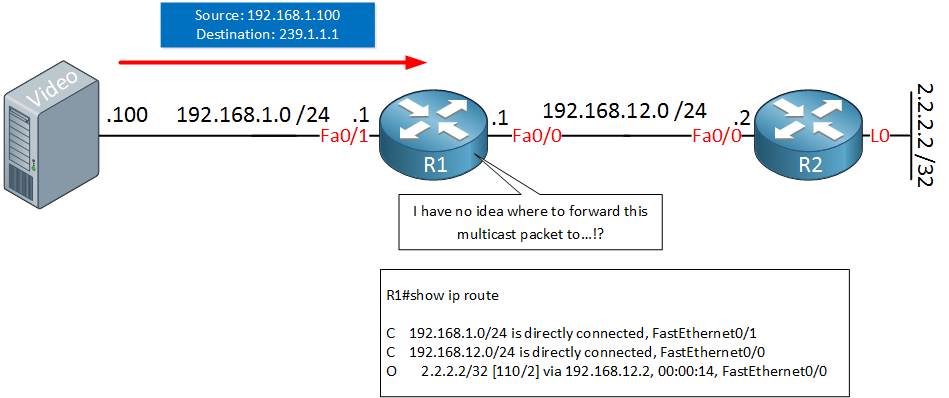
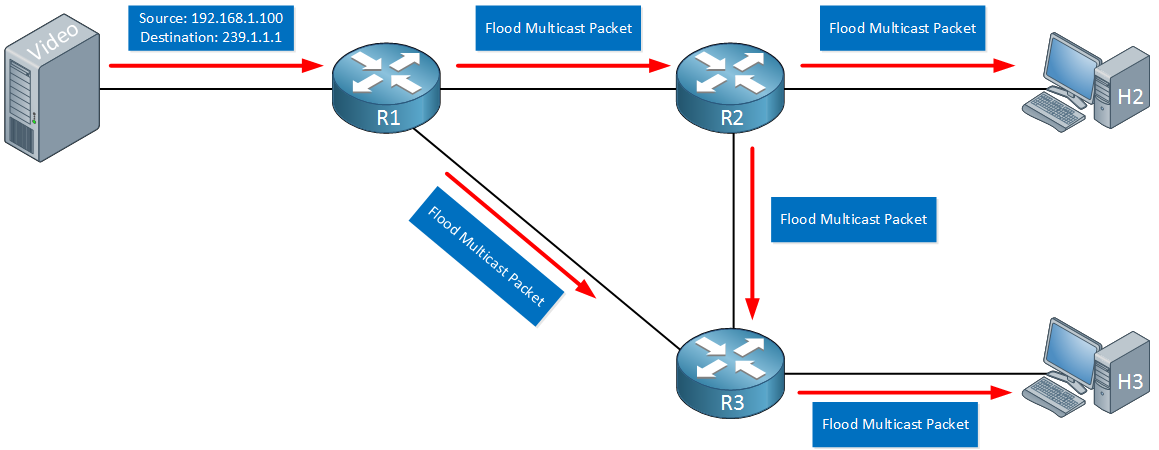
Or, if you know the multicast address used by the application that you’re interested in, you can specify that as the destination address in a capture filter such as “dst host 239.1.1.1”. If you want to capture all multicast packets, you can just use the capture filter keyword “multicast” and start capturing. The router doesn’t have any downstream neighbors that require the multicast traffic.
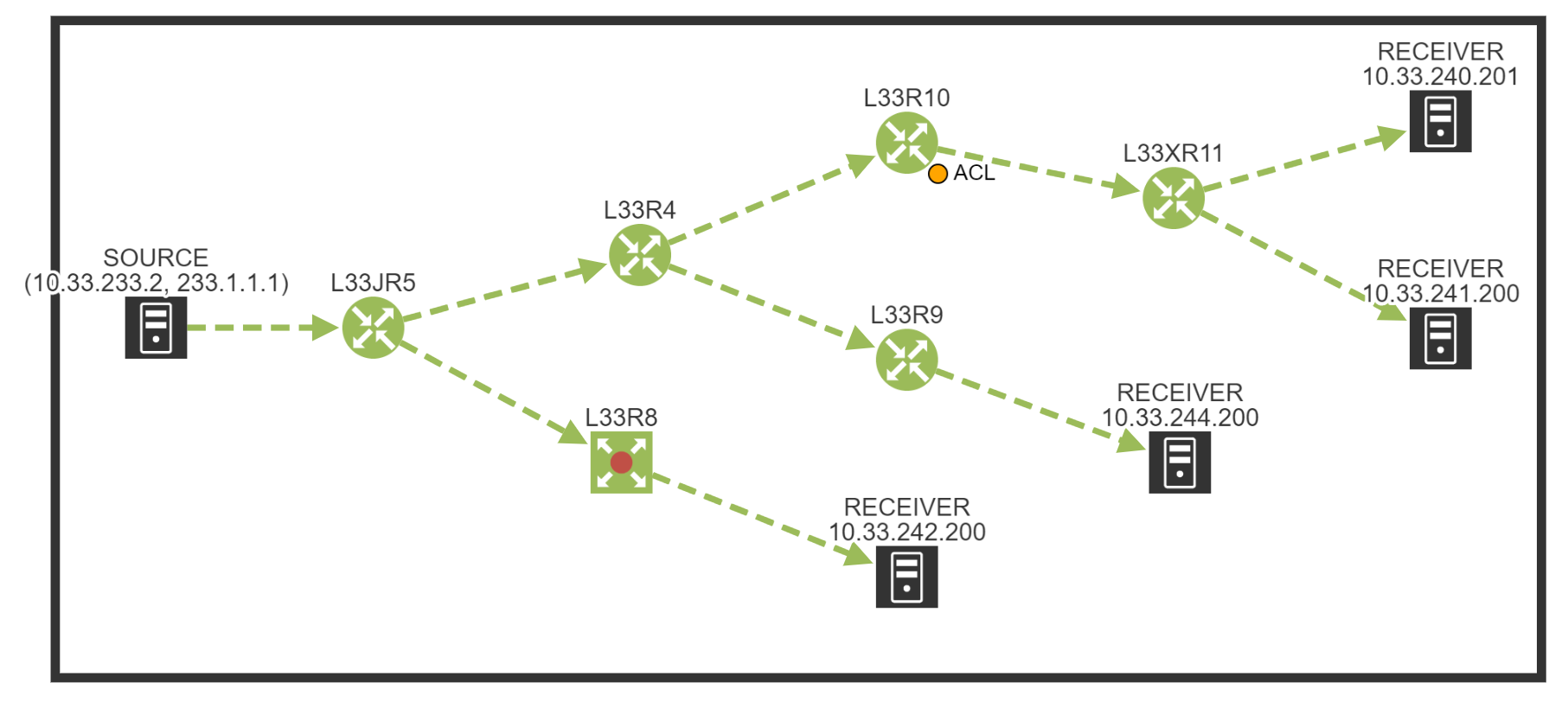
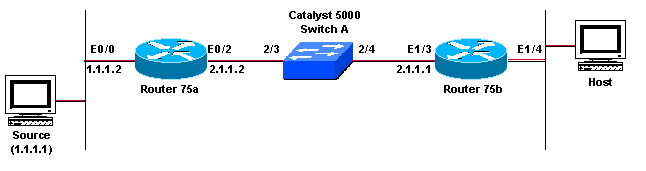
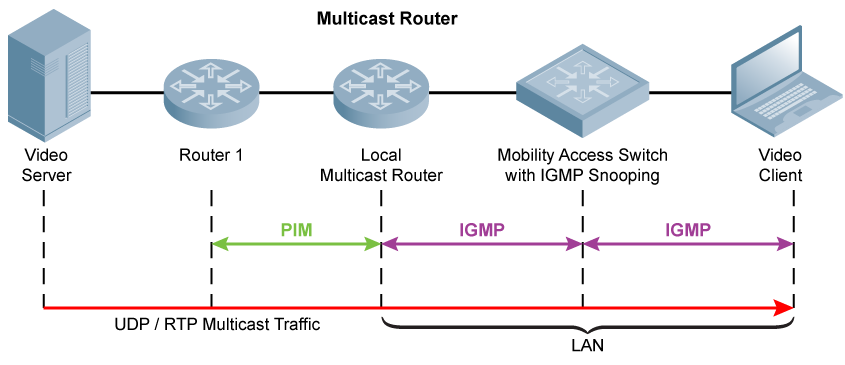
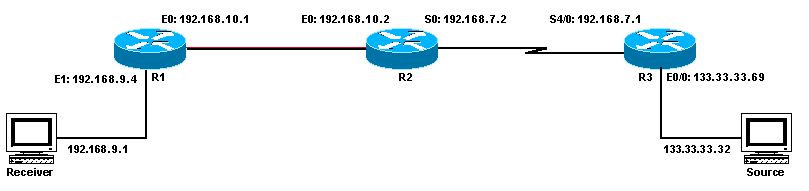
Hosts directly connected to router 75a receive the multicast feed, but hosts directly connected to router 72a do not. Thus, they must include an internet group management protocol (igmp) implementation in their tcp/ip stack. Displays ip multicast groups that have been joined on one or more interfaces.
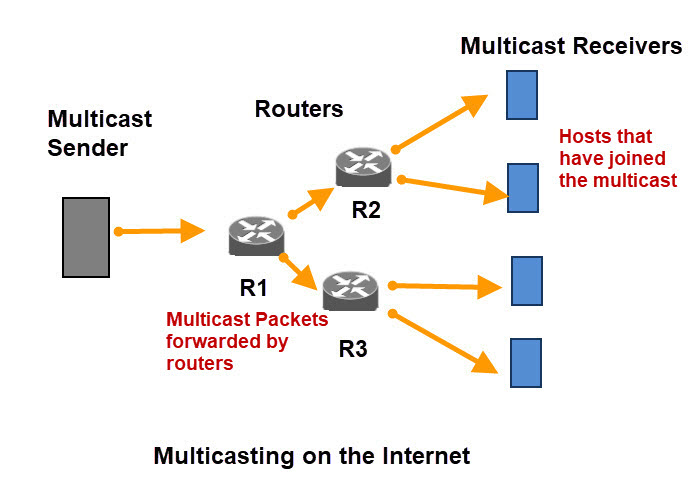
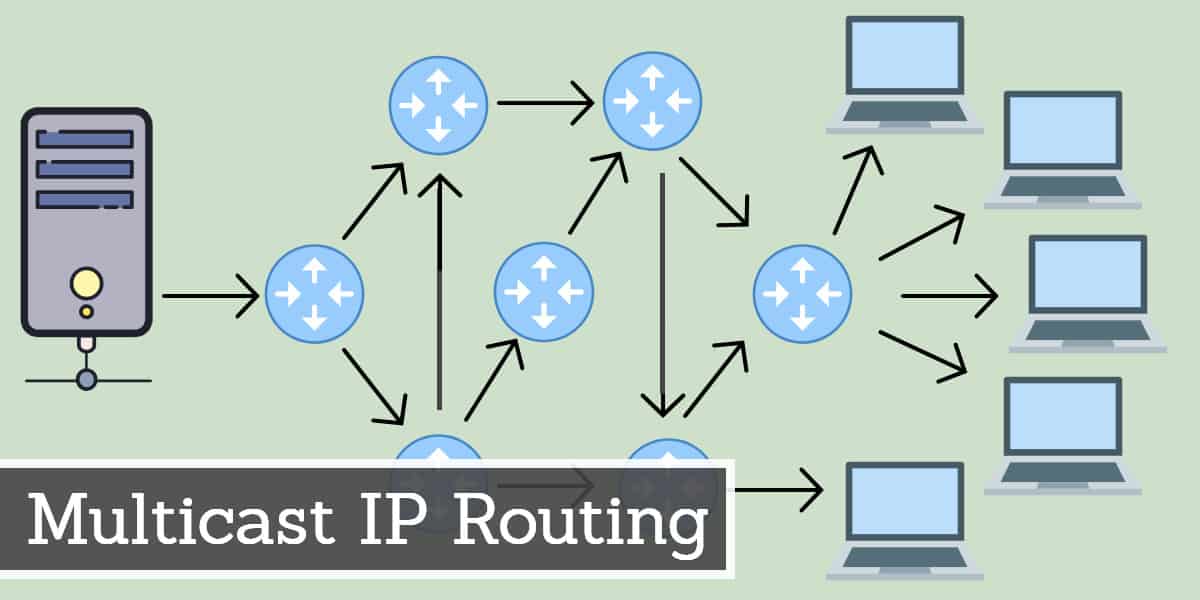
Level 2 is the full support for ip multicasting level. With multicast, we send one copy that goes to multiple different destinations. When segments don't receive the page then you'll need to test to.
To use the wsd debug client to verify multicast traffic. Sudo ip link set dev eth0. Starting with server a, determine if it has multicast address 237.0.0.1 port 9000 available for 195.0.0.1 by first checking the computer or.
Ip multicast routing is supported with multicast forwarding information base (mfib) and multicast routing. This often due to local network policy configuration. The router doesn’t have any downstream neighbors that require the multicast traffic.

![Verifying Ip Multicast Operation [Networking Software (Ios & Nx-Os)] - Cisco Systems](https://www.cisco.com/en/US/i/100001-200000/120001-130000/121001-122000/121922.jpg)